NutriPRO™ Ingredients: Enhancing Health, Wellbeing, and Performance
Posted by Lindsey Ormond, Director of Research & Development on Feb 17, 2023 5:03:29 PM
As a leader of dairy ingredient innovation, Milk Specialties Global is constantly developing and improving their product range to benefit both our customers and the consumer. Whether it be to improve processing, sensory characteristics, or bringing new health benefits to the market, the launch of our NutriPRO range is a prime example of the team’s relentless pursuit of innovative, tailored solutions to satisfy consumer desires and trends.
NutriPRO™ is range of whey protein ingredients with enhanced nutritional components, providing superior health benefits, and includes:

Whey protein is made up of several protein fractions, with bovine whey being primarily beta-lactoglobulin, then alpha-lactalbumin. Through utilizing technology and scientific advancements, the ratio of these fractions and thus enhance certain nutritive and health aspects of the fractions.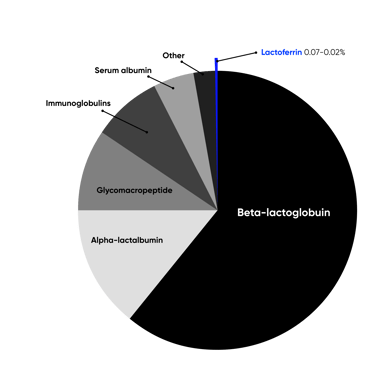
But what are these ingredients and what benefits to they provide?
LACTOFERRIN
Lactoferrin is a minor but significant whey protein fraction, naturally occurring in both human and bovine milk. It also occurs naturally in many body fluids including saliva and tears, as part of the body’s innate immune system. Lactoferrin is an iron-binding glycoprotein that binds a significant amount of iron – in fact, it binds significantly more iron than transferrin (another protein responsible for iron transport in the body). It provides health benefits across the lifespan, including:
- Gut development and immune support in infants
- Immune system support
- Favorable modulation of gut microbiome
- Improved iron status
- Antimicrobial
- Antioxidant
Research into the immune benefits of lactoferrin have demonstrated anti-bacterial, anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-viral and anti-fungal properties. While much of the research has been carried out in animal models, infants or children, there is growing support of a benefit on immune function in adults. For example, a study by Mulder et al (2008) investigated the potential immune modulating properties and antioxidant activity of oral bLF supplementation in healthy middle-aged men. The supplementation regime was 7 days of placebo, then 7 days with 100mg lactoferrin, then 7 days 200mg lactoferrin. Results showed significant increases in total T-cell activation, helper T-cell activation, cytotoxic T-cell activation and hydrophilic antioxidant capacity after 1week with 200mg lactoferrin. T cell activation stimulates a whole host of immune activities in the body, including increased surveillance and tagging of bacteria and fungi, enhanced macrophage activity and release of cytokines.

Lactoferrin has been shown to improve iron status in both female athletes and in expectant mothers. Koikawa et al (2008) supplemented female long-distance runners for 8 weeks with either lactoferrin plus iron or iron alone. To add a bit of context, female long-distance runners are frequently at risk of iron-deficiency anaemia. What they found was that women given lactoferrin and iron supplements had significantly better serum iron, ferritin and RBC counts after the intervention compared to iron only supp. Meanwhile, Paesano et al (2006) looked at another population where iron is critical – pregnant women. In this study, iron-deficient women were provided either lactoferrin iron (100mg lactoferrin with 30% iron saturation) twice daily before a meal or iron sulfate. The results showed that lactoferrin increased haemoglobin and serum iron to a greater extent than in iron sulfate supplementation. The amount of total iron from the supplements differed, with the lactoferrin group having significantly less than the iron sulfate group, yet achieving a better outcome.
ALPHA-LACTALBUMIN
Next up is alpha-lactalbumin. As the second most abundant fraction in bovine whey and the most abundant in human milk, it also provides key nutrition support across infants and adults. One of alpha’s key features is that it is higher in the essential amino acid, tryptophan, which plays a role in serotonin synthesis.
The uptake of the serotonin precursor, tryptophan, into the brain is dependent on nutrients that influence the cerebral availability of tryptophan via a change in the ratio of plasma tryptophan to the sum of the other large neutral amino acids (Trp-LNAA ratio). Therefore, a diet-induced increase in tryptophan availability may increase brain serotonin synthesis and improve coping and mood, particularly in stress-vulnerable subjects.
This has also been tested in clinical trials. Researchers tested whether evening consumption of -lactalbumin protein increased plasma Trp:LNAA, improved alertness and performance on the morning after sleep, particularly in subjects with sleep complaints. Healthy subjects with or without mild sleep complaints participated in a double-blind, placebo-controlled study. The subjects slept at the laboratory for 2 separate nights so that morning performance could be evaluated after an evening diet containing either tryptophan-rich -lactalbumin or tryptophan-low placebo protein. Researchers found that evening -lactalbumin intake caused a 130% increase in Trp:LNAA before bedtime and modestly but significantly reduced sleepiness and improved brain-sustained attention processes, as shown by the number of errors on a cognitive test, the following morning. The differences were particularly clear in poor sleepers. On top of enhanced sleep benefits, NutriPRO alpha also provides the high-quality protein we expect from whey, which can help with muscle protein synthesis and overnight recovery.
Another trial tested whether alpha–lactalbumin would improve cognitive performance in high stress–vulnerable subjects. Looking at both high and low-stress vulnerable adults in a double-blind study, they conducted a memory scanning task after either an alpha-rich diet or sodium-caseinate rich diet. A significantly greater increase in the plasma Trp-LNAA ratio after consumption of the alpha-lactalbumin diet than after the control diet was observed; and the high-stress vulnerable group exhibited faster reaction time after alpha vs control protein. Since the plasma Trp-LNAA ratio is considered to be an indirect indication of increased brain serotonin function, the authors concluded that results suggest that dietary protein rich in -lactalbumin improves cognitive performance in stress vulnerable subjects via increased brain tryptophan and serotonin activities.
MFGM
Milk fat globule membrane is a key part of the fat portion of dairy fat and in human milk. It contains many bioactive compounds, including phospholipids, IgG and other minor protein fractions, and enables closer matching to mother's milk for infant formula manufacturers. It may also support cognitive performance and gut health in adults. MFGM contains a high level of protein (around 70%), combined with an increased level of fat and phospholipids. The phospholipid profile is similar to that found in human brain and includes phosphatidyl serine, phosphatidyl choline and many more. The clinical evidence in adults around phospholipids is limited but gaining traction.
For example, one study investigated whether the daily intake of phospholipid concentrate (PL) rich in phosphatidylserine (PS) and sphingomyelin (SM) for 21 days has similar beneficial effects on working memory, in middle-aged men (Hellhammer et al, 2010). They looked at memory performance, psychological and endocrine response to a stress test in 46 healthy men (average 41.5 years) receiving either placebo or 13.5 g PL per day over a three-week period. On the 21st day of PL intake, subjects’ working memory performance and their psychological and endocrine responses to the Trier Social Stress Test (TSST) were tested. Researchers found that, compared to placebo-exposed individuals, there was a tendency for shorter reaction times in the working memory task, suggesting better performance in PL-treated subjects. Although the two treatment groups did not significantly differ in their endocrine stress response, the PL-treated subjects with a higher stress load showed a blunted psychological stress response.
CONCLUSION
Whey protein has been used as part of a healthy diet for decades, with its key benefits linked to enhancing and maintaining muscle mass. However, by utilizing technology, the NutriPRO range of ingredients provides even greater health benefits from this unique, natural protein.
Contact a member of the team, visit us at Expo West or complete the contact form for more information on how you can utilize this ingredient range to satisfy consumer needs and desires for natural solutions.
Topics: HUMAN NUTRITION
