NutriPRO™ Ingredients: Enhancing Health, Wellbeing, and Performance
Posted by Lindsey Ormond, Director of Research & Development on Feb 17, 2023 5:03:29 PM
As a leader of dairy ingredient innovation, Milk Specialties Global is constantly developing and improving their product range to benefit both our customers and the consumer. Whether it be to improve processing, sensory characteristics, or bringing new health benefits to the market, the launch of our NutriPRO range is a prime example of the team’s relentless pursuit of innovative, tailored solutions to satisfy consumer desires and trends.
Read MoreTopics: HUMAN NUTRITION
Enhancing Weight Management with Whey Protein and Alpha-lactalbumin
Posted by Lindsey Ormond, Director of Research & Development on Dec 20, 2022 3:46:04 PM
Topics: HUMAN NUTRITION
Protein: Back to Basics
Posted by Lindsey Ormond, Director of Research & Development on Jun 21, 2022 4:47:37 PM
Topics: HUMAN NUTRITION
NUTRITION CHALLENGES FOR AGING: THE IMPACT OF PROTEIN ON SATIETY AND ENERGY INTAKE
Posted by Daniel Crabtree, PhD on May 16, 2022 9:35:14 AM
Topics: HUMAN NUTRITION
CAN LACTOSE BE A GOOD FUEL SOURCE FOR ATHLETES?
Posted by Lindsey Ormond, Director of Research & Development on Feb 9, 2022 4:27:56 PM
Our bodies utilize carbohydrates both from the diet (exogenous), and our body stores to provide energy for exercise, particularly prolonged endurance exercise. Carbohydrate is stored in our liver and muscles in the form of glycogen, but there is a limit to how much can be stored. When endogenous stores are depleted, fatigue kicks in and athletes can “hit the wall” if exogenous sources aren’t available. Delaying the depletion of the body’s carbohydrate stores by consuming carbohydrate during exercise is a beneficial tactic for prolonging and enhancing exercise performance. Increasing the use of fat as a fuel (fat oxidation) may also be beneficial for improving exercise performance and delaying depletion of the body’s carbohydrate stores.
Read MoreTopics: HUMAN NUTRITION
WHEY CAN INCREASE PROTEIN LEVELS WITHOUT NEGATIVELY IMPACTING OVERALL DIETARY INTAKE IN OLDER ADULTS
Posted by Lindsey Ormond, Director of Research & Development on Dec 23, 2021 9:39:07 AM
Sarcopenia – the loss of muscle mass and strength that occurs naturally with aging – can be mitigated by ensuring sufficient protein intake. Reducing the rate of muscle loss is a key factor for maintaining a free and active lifestyle in the advancing years. However, since protein is the most satiating nutrient and appetite diminishes with age, it could be supposed that adding more protein to the diet could lead to an overall reduction in calorie and nutrient intake at a time when they are critical.
Read MoreTopics: HUMAN NUTRITION
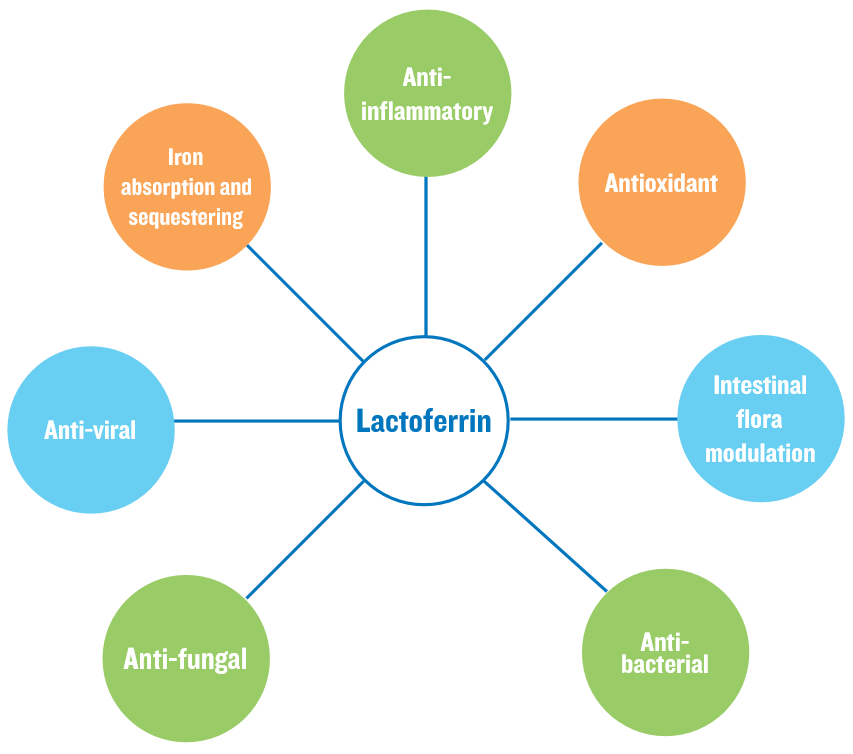
LACTOFERRIN’S ROLE IN IMMUNE SUPPORT
Posted by Lindsey Ormond, Director of Research & Development on May 6, 2021 3:28:40 PM
Topics: HUMAN NUTRITION
Alpha-lactalbumin: Enabling Higher Quality Infant Formula
Posted by Research & Development on Nov 6, 2020 11:05:23 AM
Breastfeeding is recommended by the World Health Organization as the best option for the developing infant1. Where breastfeeding is not possible, infant formulas provide a nutritious substitute, with advances in technology enabling more sophisticated formulas to be produced.
Both human and bovine milk are complex matrices of nutrients and bioactive compounds, developed by nature to support growth and development. The protein in both human and bovine milk is composed of two main types: whey and casein, although the ratio of these varies between species; from 60:40 whey:casein in mature human milk, to 20:80 in cows’ milk. Both types of proteins are high quality, meaning they have an excellent essential amino acid profile that is well digested and absorbed by the body.
Read MoreTopics: HUMAN NUTRITION
FORMULATING WITH CLEAR WHEY PROTEIN
Posted by Jennifer Roberts, R&D Product Development Scientist on Sep 22, 2020 9:13:21 AM
Protein products have dominated store shelves for several years now – everything from protein bars to shakes, chips to baking mixes. Protein, specifically proteins from milk, have been shown to reduce risk factors for cardiovascular disease1 and improve overall satiety2. They’re also great for muscle recovery, on-the-go nutrition, and create functional benefits for a multitude of food categories. So, what is driving innovation in this market? Clear proteins. These proteins are capable of fortifying new categories of functional foods. They can be utilized at a range of concentrations, processes, and provide a clean and fresh flavor. In this blog, we’ll explore the benefits of clear whey proteins, how to use them, important formulation and processing considerations, and highlight PRObev™, our award-winning protein that is a leader in the clear protein category.
Read MoreTopics: HUMAN NUTRITION
HOW WHEY PROTEINS SUPPORT THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
Posted by Research & Development on Aug 21, 2020 8:30:31 AM
The influence that whey proteins can have on the immune system is an area of growing interest and, with more consumers seeking ways to support their immune system, it’s no surprise that the demand for such ingredients are on the rise.
WHEY PROTEIN
Whey protein is renowned for its muscle building ability, given its unrivalled composition and digestibility characteristics. Think about it – whey protein has all nine essential amino acids, is high in leucine, a great source of branched-chain amino acids, and absorbs quickly, not least due to its high digestibility. It supports strong bodies from a strength perspective (of course, in combination with exercise) and can also assist in weight management goals due to its role in increasing satiety. While whey protein supports these goals, it is more than just muscle building and weight management for your body. The immune system support starts with a healthy, balanced diet, with favorable body weight and composition, and an active lifestyle.
Whey protein is made up of protein fractions, as shown in Figure 1, and each fraction can exert different health benefits. In fact, two key fractions in immune system support are:
- Lactoferrin
- Immunoglobulins
Topics: HUMAN NUTRITION