CAN LACTOSE BE A GOOD FUEL SOURCE FOR ATHLETES?
Posted by Lindsey Ormond, Director of Research & Development on Feb 9, 2022 4:27:56 PM

Our bodies utilize carbohydrates both from the diet (exogenous), and our body stores to provide energy for exercise, particularly prolonged endurance exercise. Carbohydrate is stored in our liver and muscles in the form of glycogen, but there is a limit to how much can be stored. When endogenous stores are depleted, fatigue kicks in and athletes can “hit the wall” if exogenous sources aren’t available. Delaying the depletion of the body’s carbohydrate stores by consuming carbohydrate during exercise is a beneficial tactic for prolonging and enhancing exercise performance. Increasing the use of fat as a fuel (fat oxidation) may also be beneficial for improving exercise performance and delaying depletion of the body’s carbohydrate stores.
Most carbohydrate-electrolyte products aimed at providing energy during exercise contain a rapidly absorbed carbohydrate, such as glucose, maltodextrin, sucrose or a combination of glucose and fructose. Lactose is composed of glucose + galactose, but since the latter is utilized at a much slower rate than glucose, it hasn’t been top choice during exercise and research has tended to focus on other energy sources. But could that be set to change?
In a recent study from the University of Birmingham, UK, researchers looked at whether lactose could be utilized as a fuel source during exercise, and how this compared to sucrose1. During a 2.5hr moderate intensity cycling exercise, participants consumed 48g per hour of carbohydrate from sucrose or lactose, or water alone. They then analyzed what fuel the body used from both endogenous and exogenous sources. The main findings were that:
- Lactose was utilized as a fuel source at a similar rate to sucrose
- Lactose increased use of fat as a fuel (fat oxidation – see figure 1)
- Lactose reduced use of endogenous carbohydrate stores, thereby sparing the body’s carbohydrate stores (glycogen), a benefit that may enhance performance
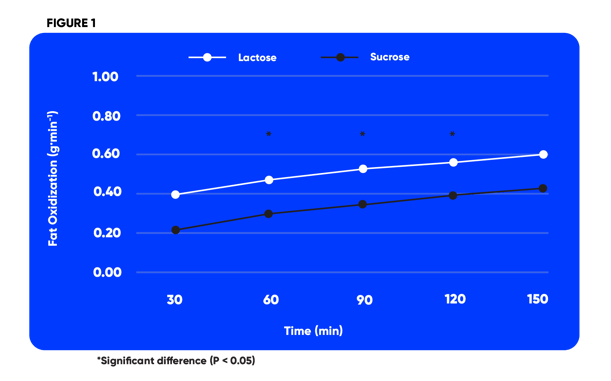
With these beneficial effects on which fuels are utilized and spared during exercise, lactose could be an advantageous fuel source during exercise, enhancing fat use and sparing the body’s carbohydrate stores, which could ultimately impact on performance.
Odell OJ, Podlogar T, Wallis GA. Comparable Exogenous Carbohydrate Oxidation from Lactose or Sucrose during Exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2020;52(12):2663-2672. doi:10.1249/MSS.0000000000002426
Topics: HUMAN NUTRITION
