Research & Development
Recent Posts
Alpha-lactalbumin: Enabling Higher Quality Infant Formula
Posted by Research & Development on Nov 6, 2020 11:05:23 AM
Breastfeeding is recommended by the World Health Organization as the best option for the developing infant1. Where breastfeeding is not possible, infant formulas provide a nutritious substitute, with advances in technology enabling more sophisticated formulas to be produced.
Both human and bovine milk are complex matrices of nutrients and bioactive compounds, developed by nature to support growth and development. The protein in both human and bovine milk is composed of two main types: whey and casein, although the ratio of these varies between species; from 60:40 whey:casein in mature human milk, to 20:80 in cows’ milk. Both types of proteins are high quality, meaning they have an excellent essential amino acid profile that is well digested and absorbed by the body.
Read MoreTopics: HUMAN NUTRITION
HOW WHEY PROTEINS SUPPORT THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
Posted by Research & Development on Aug 21, 2020 8:30:31 AM
The influence that whey proteins can have on the immune system is an area of growing interest and, with more consumers seeking ways to support their immune system, it’s no surprise that the demand for such ingredients are on the rise.
WHEY PROTEIN
Whey protein is renowned for its muscle building ability, given its unrivalled composition and digestibility characteristics. Think about it – whey protein has all nine essential amino acids, is high in leucine, a great source of branched-chain amino acids, and absorbs quickly, not least due to its high digestibility. It supports strong bodies from a strength perspective (of course, in combination with exercise) and can also assist in weight management goals due to its role in increasing satiety. While whey protein supports these goals, it is more than just muscle building and weight management for your body. The immune system support starts with a healthy, balanced diet, with favorable body weight and composition, and an active lifestyle.
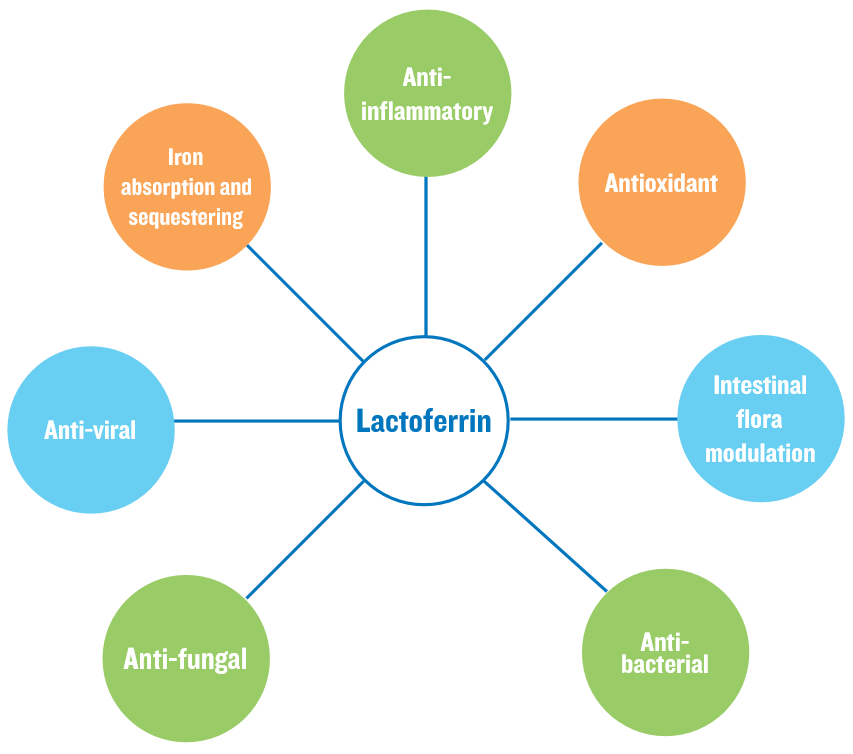
Whey protein is made up of protein fractions, as shown in Figure 1, and each fraction can exert different health benefits. In fact, two key fractions in immune system support are:
- Lactoferrin
- Immunoglobulins
Topics: HUMAN NUTRITION
Milk Specialties Global is boosting the North American supply chain with Calcium Caseinate sourced and produced in the United States. The rBGH free skim milk is sourced from California dairy farms and transported to the Visalia, CA facility to produce Calcium Caseinate.
Calcium Caseinate is a highly functional ingredient with an excellent amino acid profile. It has excellent dispersibility, viscosity, and emulsification capabilities; making it a versatile ingredient of choice for ready to mix sports nutrition powders and other functional food applications.
The process of producing Calcium Caseinate involves gentle acidification and neutralization of the milk to help retain all superior nutritional qualities. Calcium Caseinate is an extremely nutritious and clean tasting ingredient that delivers a high level of protein with low levels of carbohydrates (sugar/lactose). It is also high in naturally occurring calcium phosphate which is the building block for strong teeth and bones, helping to maintain bone density and structural functions.
Milk Specialties Global’s Calcium Caseinate is available in instant and regular form, with non-GMO, Non-GMO Project Verified, Kosher and Halal certifications. Instant Calcium Caseinate is recommended for use in all nutritional powder formulations to improve nutritional and sensory attributes as well as increase the product shelf-life.
To learn more about Milk Specialties Global’s Calcium Caseinate and our extensive dairy protein portfolio, contact your Milk Specialties Account Manager or email us directly at ingredientsales@milkspecialties.com.
Read MoreTopics: HUMAN NUTRITION