LACTOFERRIN’S ROLE IN IMMUNE SUPPORT
Posted by Lindsey Ormond, Director of Research & Development on May 6, 2021 3:28:40 PM
WHAT IS LACTOFERRIN?
Lactoferrin is a small but mighty globular glycoprotein found in human, bovine, and other mammalian milk. The physiological functions of lactoferrin are extensive and mainly immune-related - from antifungal, antiviral and antibacterial, to iron absorption, to antioxidant and microbiome modulation.
BENEFITS OF LACTOFERRIN
Lactoferrin in breastmilk and formula provides immune support for the growing infant, both in terms of protecting the infant from harmful pathogens and facilitating the infant's own immune development. However, the benefits of lactoferrin extend beyond the initial year of life, as clinical trials have shown lactoferrin supplementation can support the immune systems of both children and adults.
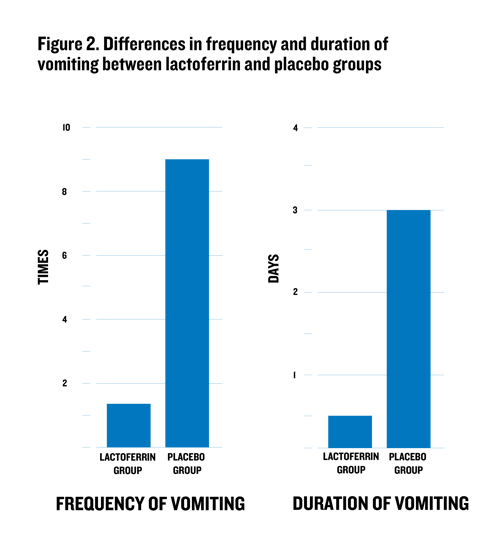
The impact of lactoferrin on gastrointestinal health was demonstrated in one study looking at the influence of 100mg lactoferrin supplementation on rotavirus gastroenteritis incidence in children under 5 years old in a daycare setting1. The researchers found that, although daily supplementation for 12-weeks did not reduce the incidence of rotaviral gastroenteritis, it did significantly lower the frequency and duration of vomiting and diarrhea compared to the placebo group, as shown in figure 2.
In adults, a reduction of common cold-like symptoms was reported in women who supplemented their daily diets with 600mg lactoferrin for 3 months2. These findings were supported by another research group in a double-blind randomized trial the following year3. Daily supplementation for 3 months of 400mg lactoferrin plus 200mg IgF was found to significantly reduce the number of colds by more than half compared to placebo (0.93 vs 2.26, respectively p <0.001).
More recently, lactoferrin’s renowned antiviral properties have been tested against SARS-CoV-2. In one in vitro study, researchers assessed lactoferrin’s potential for preventing SARS-CoV-2 infection by observing the antiviral immune response gene expression in Caco-2 intestinal epithelial cells4. They reported that treating the cells with lactoferrin enhanced their cells' antiviral response and partially inhibited the ability of the virus to infect the cells.
Other work in this area highlighted lactoferrin’s potential protective effect in SARS-CoV-2 in vivo. A research group in Italy compared both in vitro and in vivo5. A research group in Italy compared COVID-19 patients supplemented with just lactoferrin (LF), versus those receiving standard pharmaceutical treatment (SOC), versus those receiving no treatment (C). Interestingly, the length of time for subjects to convert to a negative PCR test was significantly less in the lactoferrin group compared with both other groups (14.25 LF vs 27.13 SPT vs 32.61), suggesting a reduction in the infectious period. Recovery from clinical symptoms associated with COVID-19 was also faster with lactoferrin supplementation compared to both other groups, indicating lactoferrin could be beneficial in the management of this disease.
POTENTIAL MECHANISMS OF ACTIONS
Lactoferrin has a high affinity for metal ions, particularly iron, and this ability to bind and sequester iron has been noted as the main mechanism contributing to lactoferrin’s antimicrobial properties. One possible explanation for lactoferrin’s ability to protect against pathogens, including E. coli, E. sakazakii, Hepatitis C, and rotavirus, is that it competes with the bacteria for iron, thus inhibiting its growth.
Another potential mechanism linked to lactoferrin’s antimicrobial properties is that it binds to receptors on the host cells, thus competing with viruses for cell adhesion and blocking them from binding to and entering the host cell4,6. Lactoferrin has been shown to prevent microorganisms from adhering to, colonizing, and forming a biofilm on host cells7. The formation of biofilm is a crucial step in the development and persistence of infection.
Furthermore, lactoferrin has been suggested to have a prebiotic benefit in the large intestine. Upon digestion of lactoferrin, several bioactive peptides are released, which have been shown to enhance the growth of bifidobacterial8. This may be another reason why this unique whey protein fraction exerts an immunomodulatory benefit, as the gut microbiome is known to influence immune function and greater colonization with bifidobacteria may limit pathogen growth.
SUMMARY
Lactoferrin is a naturally occurring protein found in whey protein. This small but mighty whey protein fraction has been shown to have multiple health benefits across all life stages. Through a proprietary process, Milk Specialties Global is able provide a range of highly concentrated lactoferrin ingredients.
QUESTIONS? CONTACT US TODAY
OTHER ARTICLES YOU MAY BE INTERESTED IN:
REFERENCES
-
Egashira et al. Acta Paediatr. 2007 Aug;96(8):1242-4
-
Oda et al. Jpn J Complement Altern Med 2012;9:121e8
-
Vitetta et al. Complement Ther Med. 2013 Jun;21(3):164-71
-
Salaris et al. Nutrients. 2021 Jan 23;13(2):328
-
Campione et al. bioRxiv. 2020 Dec doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.08.11.244996. Preprint
-
Hu et al. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2021 Dec;10(1):317-330
-
Lönnerdal B. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2009 May;12(3):293-7
-
Liepke et al. Eur J Biochem. 2002 269:712-718
Topics: HUMAN NUTRITION
